Knee Pain: Causes, Relief, and Long-Term Solutions Reclaim Your Mobility: A Guide to Understanding and Overcoming Knee Pain
Knee pain is one of the most widespread musculoskeletal complaints affecting individuals across various age groups. It can stem from injuries, chronic health conditions, or lifestyle factors. The knee joint is a complex structure consisting of bones, cartilage, ligaments, and tendons—any of which can be a source of pain. Whether mild or severe, knee pain can reduce mobility, limit physical activity, and affect quality of life.
This comprehensive guide provides in-depth insights into the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for knee pain, helping you understand how to manage your condition and take proactive steps toward recovery.
What Is Knee Pain?
Knee pain refers to any discomfort, inflammation, or damage located in or around the knee joint. It may result from sudden injuries, medical conditions, or repetitive strain. This pain can affect different parts of the knee, including the kneecap (patella), cartilage, ligaments, and the surrounding muscles.
Types of Knee Pain
- Acute Knee Pain: Arises quickly due to trauma, such as a fall or sports injury. Symptoms are usually sharp, intense, and may include swelling or bruising.
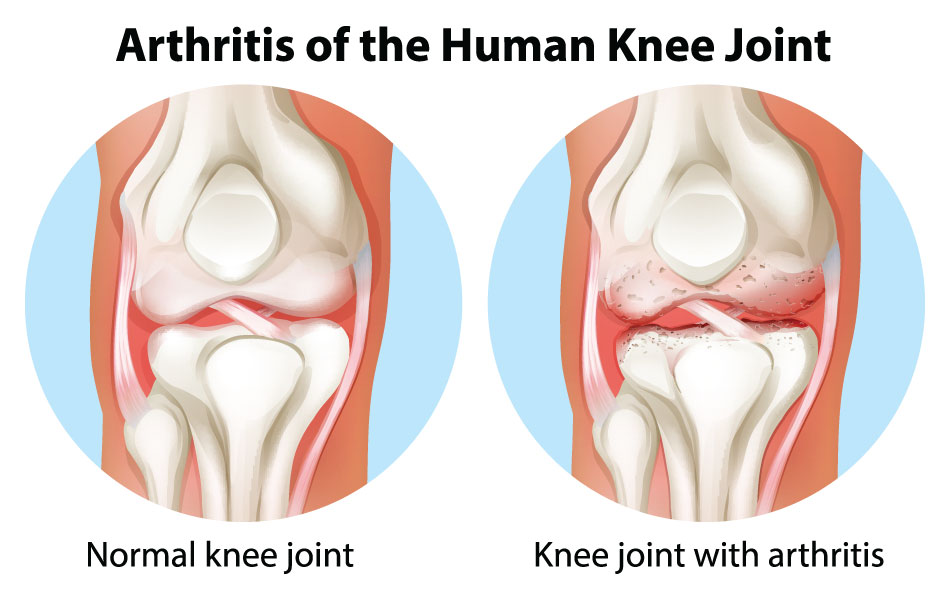
- Chronic Knee Pain: Develops gradually and persists over time, commonly due to conditions like osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or long-term overuse. It may worsen with activity or remain constant.
- Referred Pain: Originates from other parts of the body, such as the hip or lower back, but is felt in the knee. Often linked to nerve impingements or spinal issues.
Common Causes of Knee Pain
1. Injuries
Injuries are a leading cause of acute knee pain and can severely impact joint function. They often occur during physical activities or accidents.
- ACL Tears: A rupture of the anterior cruciate ligament, often from sports involving sudden stops or changes in direction. Symptoms include instability, swelling, and a popping sound at the time of injury.
- Meniscus Tears: The meniscus acts as a cushion between the femur and tibia. Tears typically occur during forceful twisting or impact. Pain is localized and may worsen with movement.
- Tendonitis: Inflammation of the tendons, particularly the patellar tendon. It results from repetitive motion or overuse, causing sharp pain below the kneecap.
- Dislocated Kneecap: Occurs when the patella slides out of its normal position, often from a direct blow or pivoting movement. It causes visible deformity and intense pain.
2. Medical Conditions
Chronic medical conditions can lead to progressive knee discomfort and mobility limitations.
- Osteoarthritis: Age-related degeneration of cartilage that causes pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility, especially in older adults.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: An autoimmune condition that leads to chronic inflammation, joint erosion, and deformity if left untreated.
- Gout: Caused by a buildup of uric acid crystals in the joint, leading to sudden, severe episodes of pain, swelling, and redness.
- Bursitis: Inflammation of the bursae, small sacs that cushion the knee. It may result from repeated kneeling, infection, or trauma.
3. Mechanical Problems
Altered biomechanics and joint misalignments can stress the knee and surrounding tissues.
- Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome: Pain at the front of the knee, often worsened by stair climbing, squatting, or prolonged sitting.
- Iliotibial Band Syndrome: Inflammation caused by the IT band rubbing against the outer knee. Common among distance runners.
- Hip or Foot Issues: Misalignment or dysfunction in these areas can shift strain to the knee, causing pain over time.
Symptoms to Watch For
Monitoring symptoms helps identify the seriousness and cause of knee pain.
- Swelling and stiffness: Indicate inflammation, injury, or arthritis.
- Redness or warmth: May be signs of infection or acute inflammatory conditions.
- Weakness or instability: Suggests ligament damage or neuromuscular issues.
- Popping or crunching sounds: May result from torn cartilage or degenerative changes.
- Inability to straighten the knee: Can indicate mechanical blockages or severe injury.
Diagnosis and Evaluation
Accurate diagnosis is essential for effective treatment. A healthcare provider may perform:
- Physical Examination: Includes assessing joint mobility, strength, swelling, and tenderness.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays to detect bone fractures, MRIs for detailed views of soft tissues, and CT scans for structural abnormalities.
- Lab Tests: May include blood tests for inflammatory markers or aspiration of joint fluid to detect infection or crystals (gout).
Treatment Options for Knee Pain
1. Non-Surgical Treatments
a. Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation (RICE)
Effective in the first 48 hours after injury to manage pain, reduce swelling, and prevent further damage.
b. Medications
- NSAIDs: Ibuprofen or naproxen can relieve pain and inflammation.
- Corticosteroids: May be injected directly into the joint for quick relief of severe inflammation.
c. Physical Therapy
Programs may include stretching, strengthening, and range-of-motion exercises. Therapists may also use modalities like ultrasound or electrical stimulation.
d. Bracing and Orthotics
Custom braces support the knee and limit movement during recovery. Shoe inserts correct biomechanical issues and relieve joint pressure.
2. Surgical Treatments
a. Arthroscopy
A minimally invasive technique where a small camera and tools are inserted through incisions to repair damage, such as meniscus tears or cartilage trimming.
b. Partial or Total Knee Replacement
In cases of advanced arthritis, damaged joint surfaces are replaced with prosthetic components to restore mobility and function.
c. Ligament Reconstruction
Used for torn ligaments like the ACL. Involves grafting tissue to rebuild the ligament and stabilize the joint.
Natural and Lifestyle-Based Approaches
1. Weight Management
Losing excess weight relieves pressure on the knees, especially important for people with arthritis. Even modest weight loss can yield significant relief.
2. Exercise
Choose low-impact options to strengthen muscles while protecting joints. Include resistance training to build support structures.
3. Diet
Focus on anti-inflammatory foods: leafy greens, berries, nuts, fatty fish, and whole grains. Avoid processed and high-sugar foods.
4. Supplements
- Glucosamine and Chondroitin: May help maintain cartilage health.
- Turmeric and Omega-3s: Possess anti-inflammatory properties that may ease joint pain.
5. Alternative Therapies
- Acupuncture: Stimulates nerves and releases endorphins to reduce pain.
- Massage Therapy: Enhances circulation and relieves tight muscles around the knee.
Note: Always consult a healthcare professional before beginning any supplement or alternative treatment.
When to Seek Medical Help
Seek prompt care if you experience:
- Intense or persistent pain that limits activity
- Swelling that doesn’t subside
- Inability to put weight on the leg
- Obvious deformity or signs of a serious injury
- Symptoms of infection like fever or warmth and redness around the knee
Preventing Knee Pain
To protect your knees and maintain long-term joint health:
- Stay active with appropriate exercises
- Avoid high-impact sports if prone to injury
- Warm up before activity and stretch afterward
- Use proper footwear with good arch support
- Strengthen muscles around the knee, especially the quadriceps and hamstrings
Conclusion
Knee pain is a multifaceted issue that can stem from injuries, medical conditions, or lifestyle choices. Fortunately, a wide range of treatment options—from conservative measures like physical therapy to surgical interventions—are available to help manage pain and restore function.
By understanding the cause of your knee pain and following a personalized treatment plan, you can improve your mobility, prevent further damage, and enhance your quality of life. Don’t wait for the pain to worsen. Talk to your doctor and start your recovery journey today.








